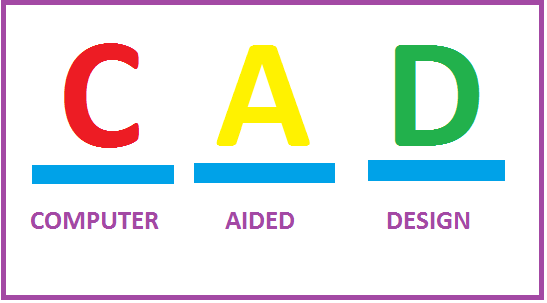
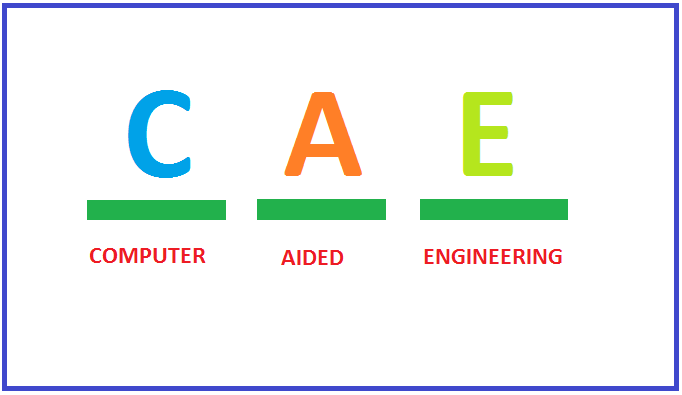
فلوئنت (Fluent) یک نرمافزار مهندسی به کمک رایانه (CAE) در زمینه دینامیک سیالات محاسباتی (CFD) برای مدل کردن جریان سیال و انتقال حرارت در هندسههای پیچیده میباشد. این نرمافزار امکان تغییر شبکه، به صورت کامل و تحلیل جریان با شبکههای غیرساختیافته برای هندسههای پیچیده را فراهم میسازد. نوع مشهای قابل تولید و دریافت توسط این گروه نرمافزاری شامل شبکههایی با المانهای مثلثی و چهارضلعی (برای هندسههای دوبعدی) و چهاروجهی، شش وجهی، هرمی یا گوهای (برای هندسههای سهبعدی) میباشد. همچنین فلوئنت به کاربر اجازه? بهبود شبکه (مثلا ریز کردن یا درشت کردن شبکه در مرزها و مکانهای لازم در هندسه) را میدهد. برای استفاده از این نرم افزار، ابتدا باید توسط یک نرم افزار کمکی مانند Gambit یا Mechanical Desktop هندسه جریان را مشخص کنید و عمل مش بندی را انجام دهید. به عبارت ساده تر، شما برای استفاده بهینه از نرم افزار فلوئنت، باید هر سه نرم افزار نام برده را نصب کنید. نرم افزار Gambit یک نرم افزار طراحی (CAD) می باشد که ورودی نرم افزار فلوئنت (Fluent) را با فرمت msh آماده می سازد. جهت استفاده از این نرم افزار نیاز به نرم افزار Exceed می باشد. Exceed نرم افزاری مدیریتی است که با اکسپلورر ویندوز تلفیق و امکان دسترسی ساده و سریع به پروفایل ها، پوشهها و اسناد نرم افزارهای Fluent و Gambit را میدهد.
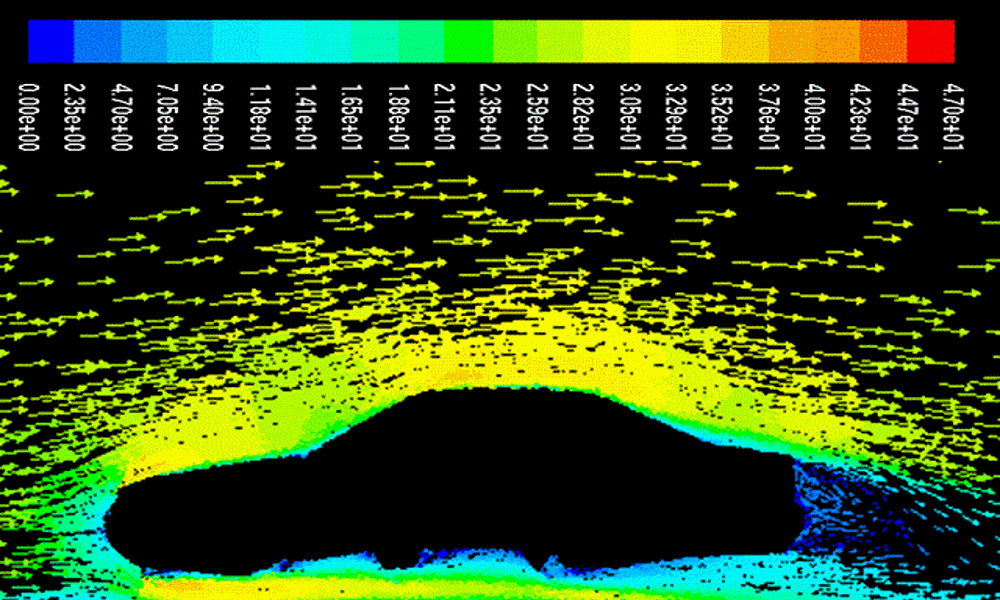
کتاب آموزش مدل سازی جریان سیال و انتقال حرارت در هندسههای پیچیده با نرم افزار FLUENT 6.3، کامل ترین کتاب در زمینه آموزش نرم افزار تحلیلی فلوئنت می باشد. این کتاب مشتمل بر 31 فصل، 2502 صفحه، به زبان انگلیسی روان، تایپ شده، به همراه کلی تصاویر رنگی، با فرمت PDF، به ترتیب زیر گردآوری شده است:
Chapter 1: Starting and Executing FLUENT
- Starting FLUENT
- Executing FLUENT Remotely
- Running FLUENT in Batch Mode
- Check pointing a FLUENT Simulation
- Cleaning Up Processes From a FLUENT Simulation
- Exiting the Program
Chapter 2: Graphical User Interface - GUI
- GUI Components
- Customizing the Graphical User Interface (UNIX Systems Only)
- Using the GUI Help System
Chapter 3: Text User Interface - TUI
- Text Menu System
- Text Prompt System
- Interrupts
- System Commands
- Text Menu Input from Character Strings
- Using the Text Interface Help System
Chapter 4: Reading and Writing Files
- Shortcuts for Reading and Writing Files
- Reading Mesh Files
- Reading and Writing Case and Data Files
- Reading FLUENT/UNS and RAMPANT Case and Data Files
- Reading and Writing Prole Files
- Reading and Writing Boundary Conditions
- Writing a Boundary Grid
- Reading Scheme Source Files
- Creating and Reading Journal Files
- Creating Transcript Files
- Importing Files
- Exporting Files
- Grid-to-Grid Solution Interpolation
- Saving Hardcopy Files
- Saving the Panel Layout
- The .fluent File
Chapter 5: Unit Systems
- Restrictions on Units
- Units in Grid Files
- Built-In Unit Systems in FLUENT
- Customizing Units
Chapter 6: Reading and Manipulating Grids
- Grid Topologies
- Grid Requirements and Considerations
- Grid Import
- Non-Conformal Grids
- Checking the Grid
- Reporting Grid Statistics
- Converting the Grid to a Polyhedral Mesh
- Modifying the Grid
Chapter 7: Boundary Conditions
- Overview of Dening Boundary Conditions
- Flow Inlet and Exit Boundary Conditions
- Pressure Inlet Boundary Conditions
- Velocity Inlet Boundary Conditions
- Mass Flow Inlet Boundary Conditions
- Inlet Vent Boundary Conditions
- Intake Fan Boundary Conditions
- Pressure Outlet Boundary Conditions
- Pressure Far-Field Boundary Conditions
Out flow Boundary Conditions - Outlet Vent Boundary Conditions
- Exhaust Fan Boundary Conditions
- Wall Boundary Conditions
- Symmetry Boundary Conditions
- Periodic Boundary Conditions
- Axis Boundary Conditions
- Fluid Conditions
- Solid Conditions
- Porous Media Conditions
- Fan Boundary Conditions
- Radiator Boundary Conditions
- Porous Jump Boundary Conditions
- Non-Reflecting Boundary Conditions
- User - Defined Fan Model
- Heat Exchanger Models
- Boundary Profiles
- Fixing the Values of Variables
- Defining Mass, Momentum, Energy, and Other Sources
- Coupling Boundary Conditions with GT-Power
- Coupling Boundary Conditions with WAVE
Chapter 8: Physical Properties
- Defining Materials
- Defining Properties Using Temperature-Dependent Functions
- Density
- Viscosity
- Thermal Conductivity
- User-Defined Scalar (UDS) Diffusivity
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Radiation Properties
- Mass Diffusion Coefficients
- Standard State Enthalpies
- Standard State Entropies
- Molecular Heat Transfer Coefficient
- Kinetic Theory Parameters
- Operating Pressure
- Reference Pressure Location
- Real Gas Models
Chapter 9: Modeling Basic Fluid Flow
- Overview of Physical Models in FLUENT
- Continuity and Momentum Equations
- User-Dened Scalar (UDS) Transport Equations
- Periodic Flows
- Swirling and Rotating Flows
- Compressible Flows
- Inviscid Flows
Chapter 10: Modeling Flows with Rotating Reference Frames

جهت دانلود کتاب آموزش مدل سازی جریان سیال و انتقال حرارت در هندسههای پیچیده با نرم افزار FLUENT 6.3 بر لینک زیر کلیک نمایید:
آموزش فلوئنت، کتاب آموزش مدل سازی جریان سیال و انتقال حرارت در هندسههای پیچیده با نرم افزار FLUENT 6.3